Understanding International Cargo Prices: A Comprehensive Guide
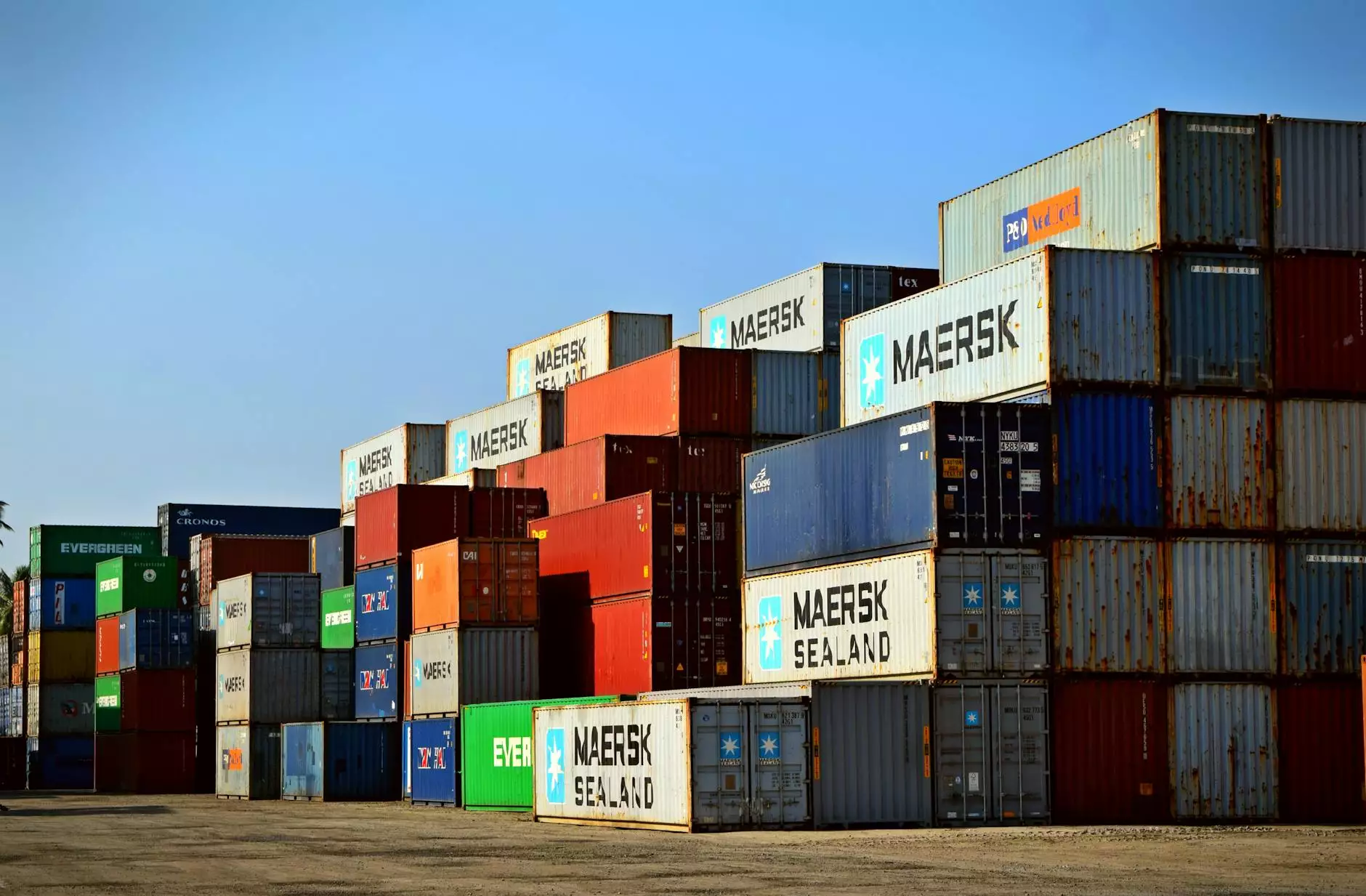

When it comes to global trade and logistics, one term you will frequently encounter is international cargo prices. These prices can vary widely depending on a multitude of factors. This guide aims to delve into the world of international cargo pricing, providing invaluable insights that can empower businesses to make informed decisions about their shipping needs.
The Basics of International Cargo Prices
Before we dive deeper, it’s crucial to understand what international cargo prices encompass. These prices refer to the costs associated with transporting goods across borders. They include several components such as:
- Freight Charges: The basic cost of moving goods from one location to another.
- Fuel Surcharges: Additional fees imposed to cover fluctuating fuel costs.
- Insurance: Protection for goods in transit against loss or damage.
- Customs Duties: Taxes imposed by governments on imported goods.
- Handling Fees: Charges for loading and unloading cargo onto and off transport vehicles.
Factors Influencing International Cargo Prices
Several variables can affect the international cargo prices you will encounter when shipping goods. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
1. Distance and Route
The distance between the origin and destination significantly impacts shipping costs. Longer routes generally incur higher freight charges due to increased fuel consumption and longer transit times. Additionally, certain routes may present logistical challenges that can further elevate shipping costs.
2. Type of Cargo
The nature of the goods being shipped also plays a critical role. For instance:
- Bulk Goods: Often more economical to ship due to lower handling costs.
- Perishable Goods: Require special handling and refrigeration, leading to higher costs.
- Hazardous Materials: Subject to stringent regulations and handling requirements, increasing their shipping prices.
3. Shipping Method
There are several modes of transportation available for international shipping:
- Air Freight: Fast but typically more expensive; best for urgent shipments.
- Ocean Freight: Cost-effective for large shipments but slower transit times.
- Land Freight: Often used for shipments to and from ports, with varying costs depending on the distance and freight type.
4. Supply and Demand
Economic fluctuations can lead to changes in supply and demand, affecting international cargo prices. For instance, during peak seasons (like holidays or major retail sales), demand surges, which may lead to higher prices. Conversely, during off-peak periods, prices might decrease as shipping companies offer discounts to attract business.
5. Currency Fluctuations
The currency in which your shipping contract is negotiated can significantly affect prices. Changes in exchange rates can either raise or lower international shipping costs, impacting overall budgets for businesses operating in a global market.